Platinum Equipment – Top Performance in Technical Use
Platinum equipment in high-quality platinum is essential in many chemical analysis laboratories. Our product range includes platinum crucibles, platinum dishes, electrodes and other laboratory equipment in various alloys, including PtAu, PtIr, PtRh and AuPd.
The alloy metals are selected depending on the specific requirements of the application. Our equipment stands out for its wetting behaviour, corrosion resistance, melting point and creep strength, which are respectively adjusted to the usage parameters. We also offer bespoke special designs. In the area of high-temperature measurements, we manufacture platinum and platinum/rhodium thermocouples in various diameters and we produce matching protective tubes. We also produce precision spinning and outlet nozzles for the fibre industry.
FKS Platinum – A Masterpiece in Fine-Grain Stabilisation
The addition of zirconium oxide hardens the platinum, produces finer grains and strengthens the structure to form a high-performance material with outstanding, material-saving properties:
- Better mechanical and chemical resistance
- Increased (up to double) tensile strength and yield strength
- Improved (up to triple) creep strength
- Increase of up to 20% in the maximum working temperature
FKS platinum has a broad range of applications in the glass industry, in laboratory equipment, in measuring technology and in special equipment manufacturing. We offer all our equipment, especially for x-ray fluorescence, both in conventional platinum alloys and in FKS platinum.
Platinum Equipment in Analytics
Platinum/Iridium 97/3, Platinum/Gold 95/5 or ZGS Platinum/Gold 95/5
Alloys of the platinum group metals (platinum, rhodium, iridium and palladium) or gold are possible as materials. Our range includes equipment for x-ray fluorescence both in traditional Pt alloys and in FKS platinum. If desired, all equipment is also available in pure platinum and silver. Please specify the desired alloy on your order.
A selection of our key models and specifications can be found here. We also offer bespoke solutions and modifications, including new developments, from our modern and flexible production. Our experts recycle pure metals in the highest purity from used crucibles, for reuse in new alloys and products.
Any damaged equipment you have can be sent to us for precious metal recovery and reworking.
If you have any further questions, please do not hesitate to call us, or click on the name of your contact to send us an enquiry.
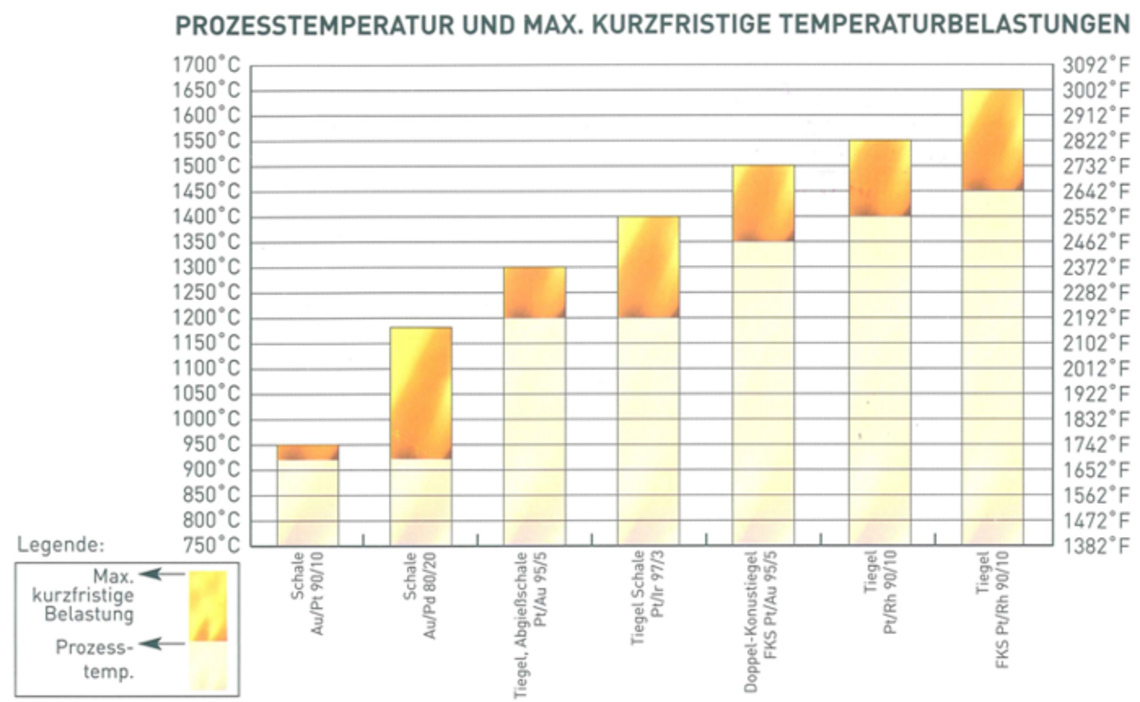
| Application | Equipment | Material | Process Temperature | Maximum Temperature | ||
| °C | °F | °C | °F | |||
| Incineration and coking of organic substances, acidic and alkaline fusion, fuming, annealing of filtration residues, thickening of liquids etc. | Crucible Dish | Pt/Ir 97/3 | 1200 | 2192 | 1400 | 2552 |
| Melting fusion | Crucible | Pt/Au 95/5 | 1200 | 2192 | 1300 | 2372 |
| Pt/Rh 90/10 | 1400 | 2552 | 1550 | 2822 | ||
| High-temperature melting fusion | Crucible Casting dish | FKS Pt | 1400 | 2552 | 1550 | 2822 |
| FKS Pt/Au 95/5 | 1350 | 2462 | 1500 | 2732 | ||
| FKS Pt/Rh 90/10 | 1450 | 2642 | 1650 | 3002 | ||
| Flour incineration | Dish | Au/Pt 90/10 | 920 | 1688 | 950 | 1742 |
| Au/Pd 80/20 | 920 | 1688 | 1180 | 2156 | ||
| Electroanalytical determination of metals, potential measurements Gravimetry, S+Cl | Electrodes | Pt/Ir 90/10 | ||||
| Schöniger electrode | Pt | |||||
The details concerning the usage recommendations are based on many years of experience in application technology. Higher temperatures, aggressive media, platinum poisons etc. can significantly influence durability. The alloys listed represent only a few of the alloys produced by Ögussa. We are happy to help if you have any questions or special requests.
Resistance Chart of the Precious Metals in Corrosive Media
| Corrosive Medium | Conditions | (°C) | (°F) | Pt | Au | Ag | Ir | Pd | Rh | Ru | Os |
| Hydrochloric acid | 36% | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 36% | 100 | 212 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Nitric acid | 65% | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Nitric acid | 65% | 100 | 212 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Sulphuric acid | 96% | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sulphuric acid | 96% | 100 | 212 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Sulphuric acid | 96% | 300 | 572 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Hydrobromic acid | 60% | 20 | 68 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Hydrobromic acid | 60% | 100 | 212 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Hydroiodic acid | 57% | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Hydroiodic acid | 57% | 100 | 212 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Hydrofluoric acid | 40% | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Phosphoric acid | 100 | 212 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| Acetic acid | 99% | 100 | 212 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Hydrochloric acid / chlorine | 20%ig/sat. | 20 | 68 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | ||||
| Hydrochloric acid / chlorine | 20%ig/sat. | 80 | 176 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Hydrochloric acid / chlorine | 20%ig/sat. | 100 | 212 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | ||
| Hydrochloric acid / bromine | 20 | 68 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |||||
| Hydrochloric acid / bromine | 100 | 212 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||||||
| Aqua regia | 20 | 68 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | ||
| Aqua regia | 100 | 212 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | ||
| Aqua regia | 150 | 302 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Hydrochloric acid / 10% H²O² | 20 | 68 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||||
| Hydrochloric acid / 10% H²O² | 100 | 212 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| Hydrobromic acid / bromine | 60% | 100 | 212 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| Water/bromine | 20 | 68 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ethanol/iodine | 20 | 68 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Sodium hypochlorite solution | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Sodium hypochlorite solution | 100 | 212 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | |
| Potassium cyanide solution | 20 | 68 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | |||||
| Potassium cyanide solution | 100 | 212 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| Copper (III) chloride solution | 100 | 212 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| Molten NaOH | Air ingress | 500 | 932 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | |
| Molten KOH | Air ingress | 500 | 932 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Molten NaOH | Air ingress | 800 | 1472 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Molten KOH | Air ingress | 800 | 1472 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Molten KHSO4 | Air ingress | 440 | 824 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Molten NaCN | Air ingress | 700 | 1292 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Molten KCN | Air ingress | 700 | 1292 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Molten NaCN/KCN (2:1) | Air ingress | 550 | 1022 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Chlorine, gaseous | Dry | 20 | 68 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chlorine, gaseous | Wet | 20 | 68 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bromine | Dry | 20 | 68 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bromine, liquid | Wet | 20 | 68 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Iodine, solid | Dry | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Iodine, solid | Wet | 20 | 68 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Fluorine, gaseous | 20 | 68 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Hydrogen sulphide, gaseous | Wet | 20 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 = No attack 2 = Slight attack 3 = Noticeable attack 4 = Destructive attack | The details are guide values, with no guarantee for a specific usage case. Edelmetall-Taschenbuch (precious metals handbook) / Degussa AG Frankfurt / Hüthig-Verlag Heidelberg, 1995 | ||||||||||